Advanced network configuration
introduces some of Docker’s advanced network configurations and options.
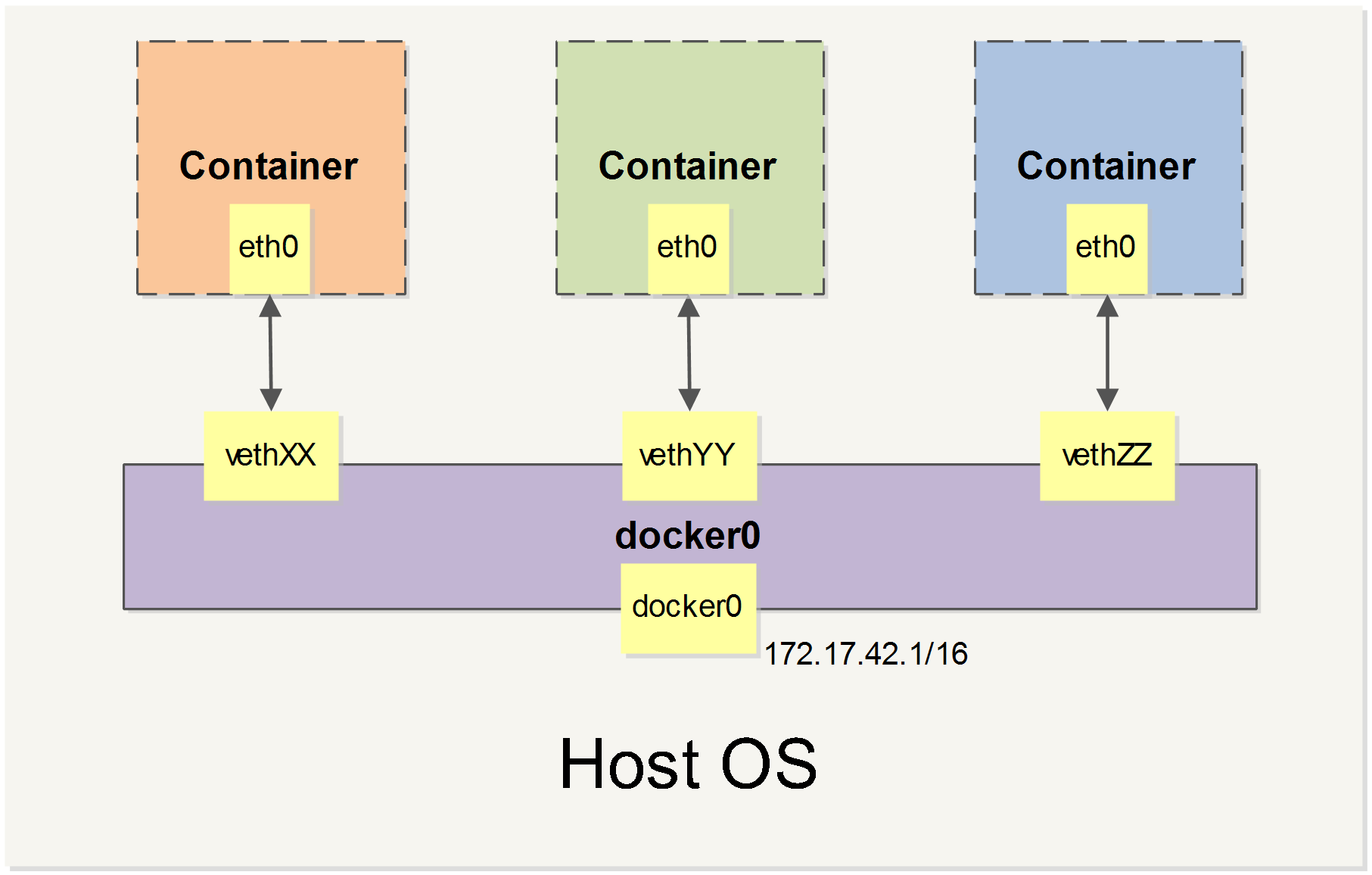
When Docker starts, it automatically creates a docker0virtual bridge on the host. It is actually a bridge of Linux, which can be understood as a software switch. It will be forwarded between the network ports that are mounted to it.
At the same time, Docker randomly assigns an address in a private unoccupied private network segment (defined in RFC1918) to the docker0 interface. For example, the typical 172.17.42.1mask of 255.255.0.0. The network port in the container started after this will also automatically assign an address of the same network segment ( 172.17.0.0/16).
When creating a Docker container, a pair of veth pair interfaces are created (when the packet is sent to one interface, the other interface can also receive the same packet). The pair is terminated in the container,eth0 ; the other end is local and mounted to the docker0 bridge, with the name starting with veth (for example, vethAQI2QT). In this way, the host can communicate with the container and the containers can communicate with each other. Docker created a virtual shared network between the host and all containers.
we will cover all of Docker’s network custom configurations in some scenarios. And adjust, complement, or even replace Docker’s default network configuration with Linux commands.
